Data Test Names
By default, the name of each test is simply the toString() on the input row.
This typically works well for data classes on the JVM but requires the input rows to be stable.
However, we can specify how the test names are generated if we are not using stable data classes, or if we are executing on a non-JVM target, or simply wish to customize.
Stable Names
When generating tests, Kotest needs a stable test name over the course of the test suite execution. The test name is used as the basis of an identifier that points to a test when notifying gradle or intellij of a test status. If the name is not stable, then the id can change, leading to errors where tests don't appear, or look like they didn't complete.
Kotest will only use the toString() of the input class if it thinks the input class has a stable toString() value
otherwise it will use the class name.
You can force Kotest to use the toString() for test names by annotating your type with @IsStableType. Then
the toString() will be used regardless.
Alternatively, you can completely customize the display name of the test.
Using a map
Kotest allows specifying test names by passing a map into the withXXX function,
where the key is the test name, and the value is the input value for that row.
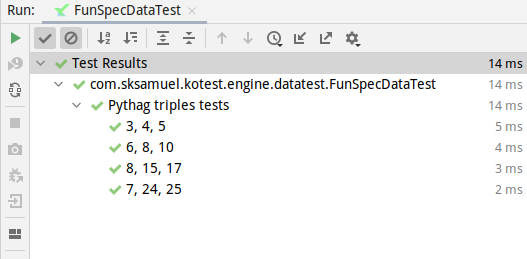
context("Pythag triples tests") {
withContexts(
mapOf(
"3, 4, 5" to PythagTriple(3, 4, 5),
"6, 8, 10" to PythagTriple(6, 8, 10),
"8, 15, 17" to PythagTriple(8, 15, 17),
"7, 24, 25" to PythagTriple(7, 24, 25)
)
) { (a, b, c) ->
a * a + b * b shouldBe c * c
}
}
Test Name Function
Or we can pass a function to withXXX which takes the row as input and return the test name. Depending on how
generous the Kotlin type inference is feeling, you may need to specify the type parameter to the withXXX function.
context("Pythag triples tests") {
withContexts<PythagTriple>(
nameFn = { "${it.a}__${it.b}__${it.c}" },
PythagTriple(3, 4, 5),
PythagTriple(6, 8, 10),
PythagTriple(8, 15, 17),
PythagTriple(7, 24, 25)
) { (a, b, c) ->
a * a + b * b shouldBe c * c
}
}
The output from this example is now slightly clearer:
WithDataTestName
Another alternative is to implement the WithDataTestName interface. When provided, the toString() will not be used,
instead the dataTestName() function from that interface will be invoked for each row.
data class PythagTriple(val a: Int, val b: Int, val c: Int) : WithDataTestName {
override fun dataTestName() = "wibble $a, $b, $c wobble"
}